In the summer of
2017, monitoring data from the Hunan hydrographic bureau showed that Hunan
recorded 20.5 days of rain in June, the accumulated average rainfall in the
province was 407.1 millimeters, which was equivalent to the waters of five
Dongting Lakes in Hunan. It broke through the historical weather records from
1951. Changsha, the provincial capital, was the region with the most severe
storms. From June 22 to July 2, the average cumulative rainfall in Changsha was
435 millimeters, exceeding 120 millimeters recorded during the 1998 flood.
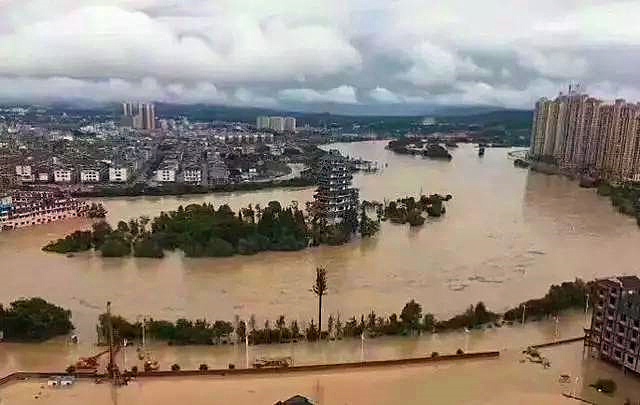

As of July 19,
this round of flooding had affected about 4,030,000 people in 1,207 villages and
towns in 115 counties (cities, districts) of 14 city states in Hunan province.
Over 310,000 people were transferred and 6,369 houses collapsed. It caused the direct
economic losses of 6 billion yuan. The direct economic loss of water
conservancy facilities was 1.37 billion yuan.
What caused the
flood? The main reason was the continuous heavy rain, which was rare in a
hundred years.
The river and
lake, as the main force for rapid diversion of rainwater, “reversed and
betrayed” at the key moment. As a result, a large number of rivers and
lakes poured into the city.
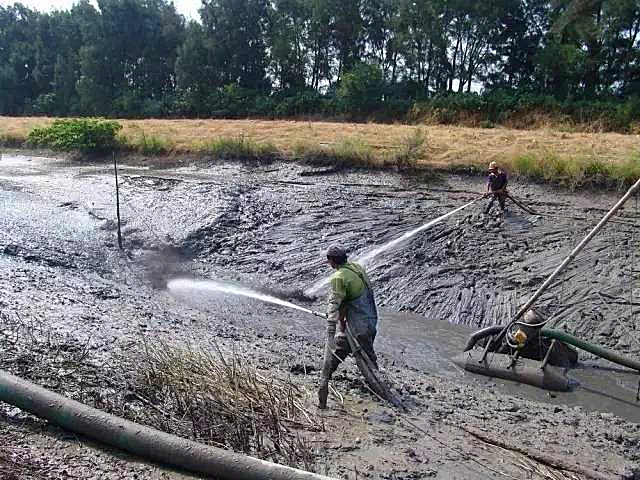

What prevents the diversion of
rivers and lakes? That must be the mud under the river and the lake. A lot of sludge deposition slowed
down the discharge of rainwater. When the floods receded, the relevant government departments
in many places in Hunan had already conducted dredging work for some rivers. How to dispose and clear the river
silt?
Because dredging of rivers and lakes
will produce a lot of high water content, high organic matter, and even
poisonous and harmful dredging mud. Therefore, the treatment and
disposal of sludge from dredging had become a hot topic of concern.
Quickly and effectively treating
and disposing the large-scale mud in the form of “reduction, harmless, and stabilization”
had become the key to the smooth implementation of urban dredging and dredging
projects.
Techase combined its own
technological advantages and provided a reasonable and efficient solution to
the problem of silt disposal in rivers and lakes under these circumstances. According to the different
conditions on the site and different customer requirements, flexible process
were adopted to realize the dredging, treatment and disposal of river silt.
Let's see how it was handled in the
end.
After the mud transported to the
shore, which were excavated by the dredger, it were processed by the garbage
sorting equipment and the sand water separation equipment. At the same time, in the event of
heavy metals and highly polluted mud, special conditioning was required. Heavy metals and high pollutants
were separated and stabilized in a timely manner. Finally it was treated by mechanical
dewatering or geotube.
Method 1, mechanical dehydration
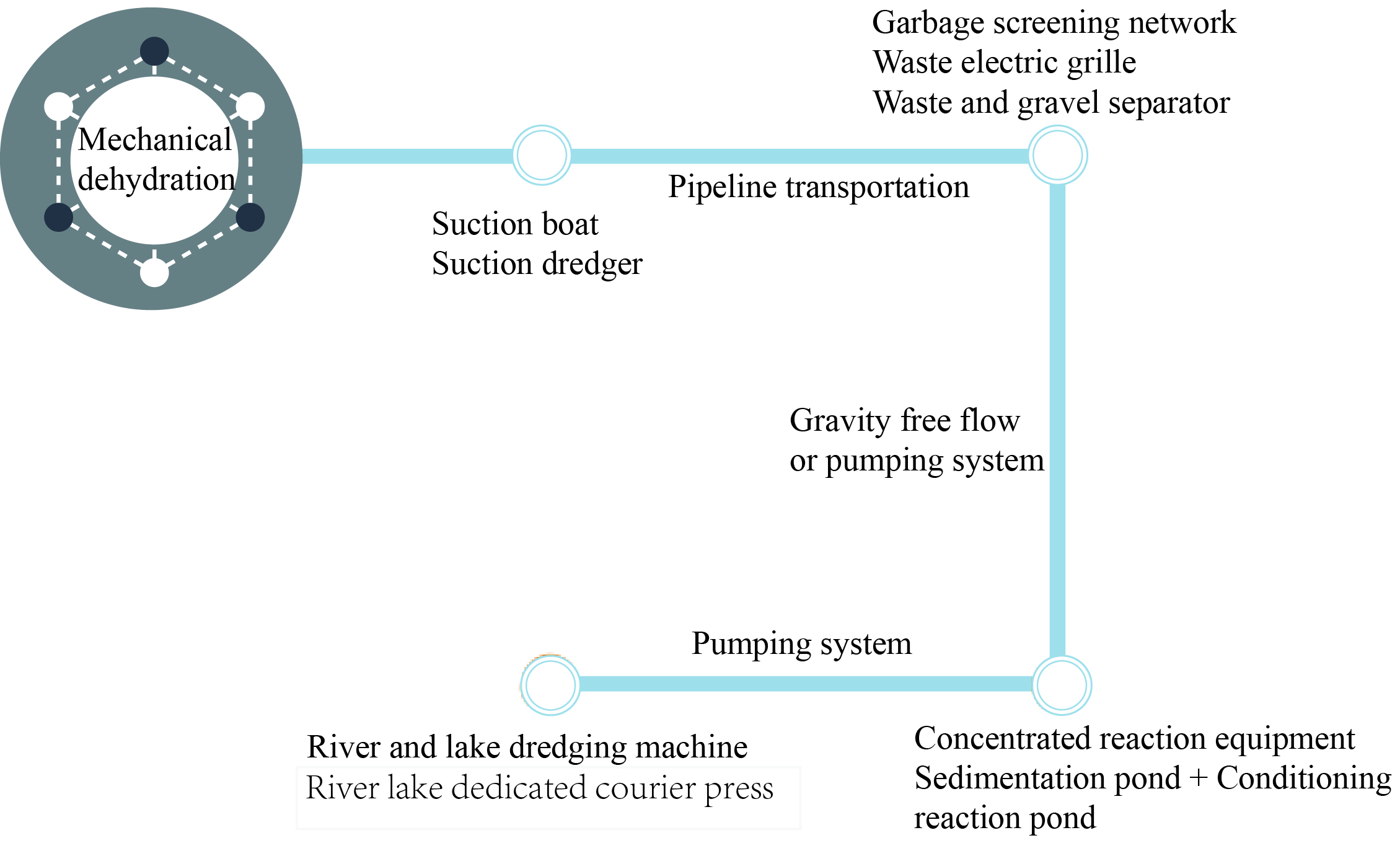
The treated mud
was pumped to a special quick press for dredging in rivers and lakes or a
special screw machine for dredging in rivers and lakes for rapid dehydration. The tail water was
returned to the water body or the tube after being settled and filtered. The dehydrated
sludge can be disposed of according to the actual conditions of the project. It can be used as
garden soil, engineering soil, building materials, etc.
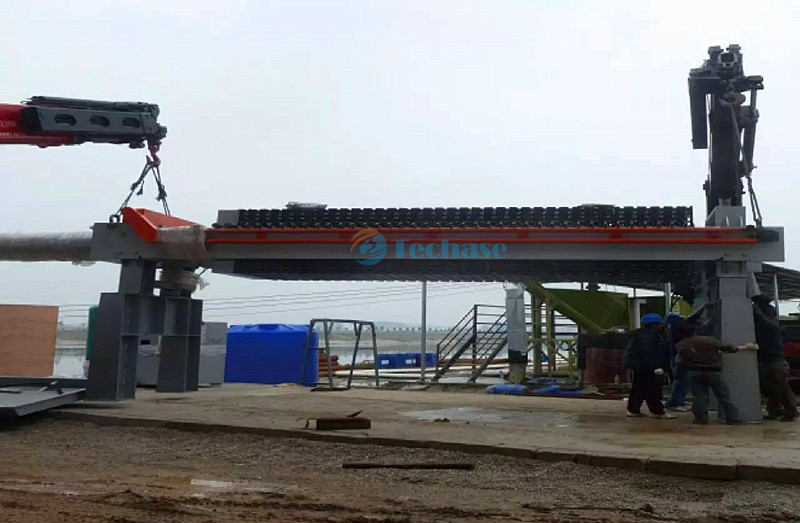

Method 2, geotube

The treated sediment was injected into the geotube. Then through flocculation, sedimentation and drain filtration, the volume can be greatly reduced. Geotube reduced the requirements of land using by multi-layered stack. The process is completely closed and pollution-free. It is a cheap and environmentally friendly method of treating sediments in rivers and lakes. Silt dehydration consolidation process eliminates the secondary pollution problem that occurs during dredging and ensures the smooth implementation of the dredging project.